Keys
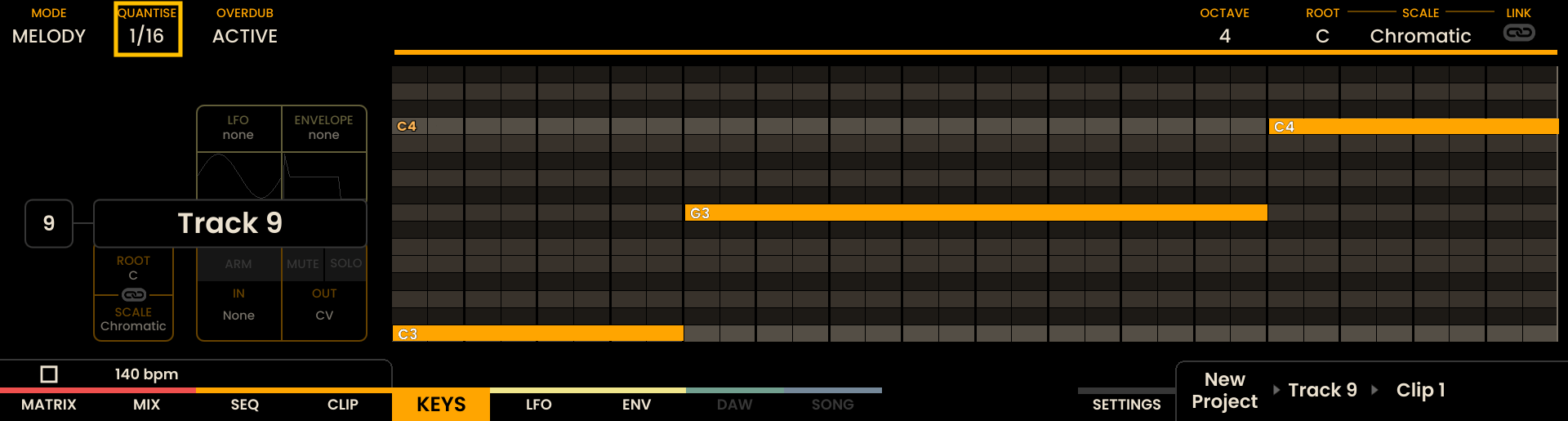
The Keys Page provides an interface for playing and recording notes and events onto a sequencer track. Various recording modes, such as overdub and quantization settings, can be defined for the selected track through the Keys page. These settings are applied to both the set track’s input settings (e.g., MIDI IN, USB) and the Keys Page itself.
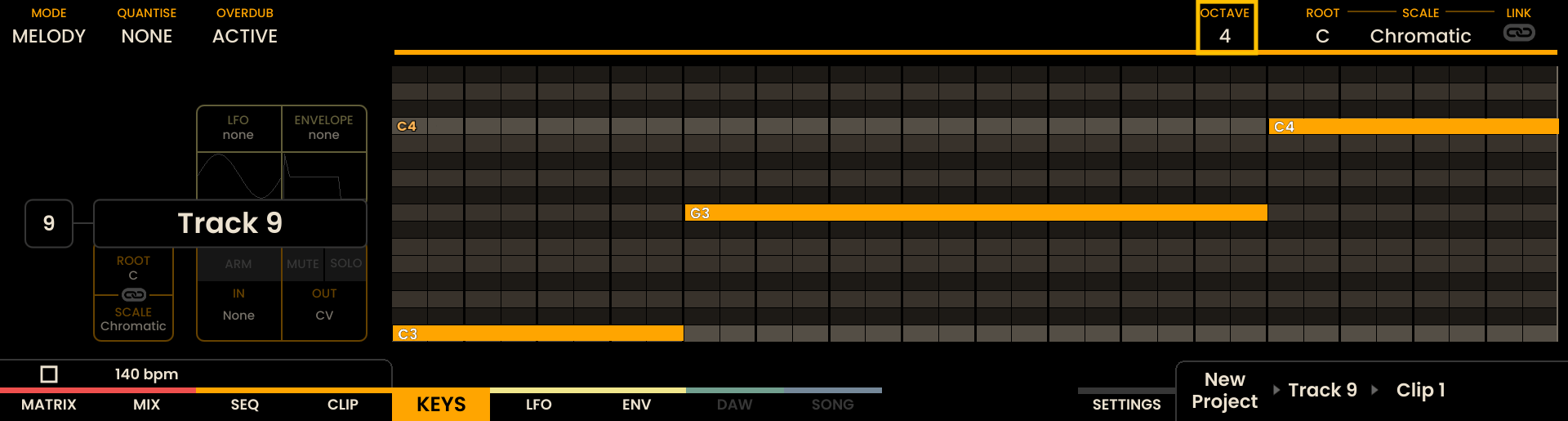
The Keys Page is equipped with several tools for real-time performance, recording, and adjustment of sequences. Different modes, including KEY and MELODY are available, each offering specific layouts and functionalities. These modes also allow for scale, root note, and transposition adjustments.
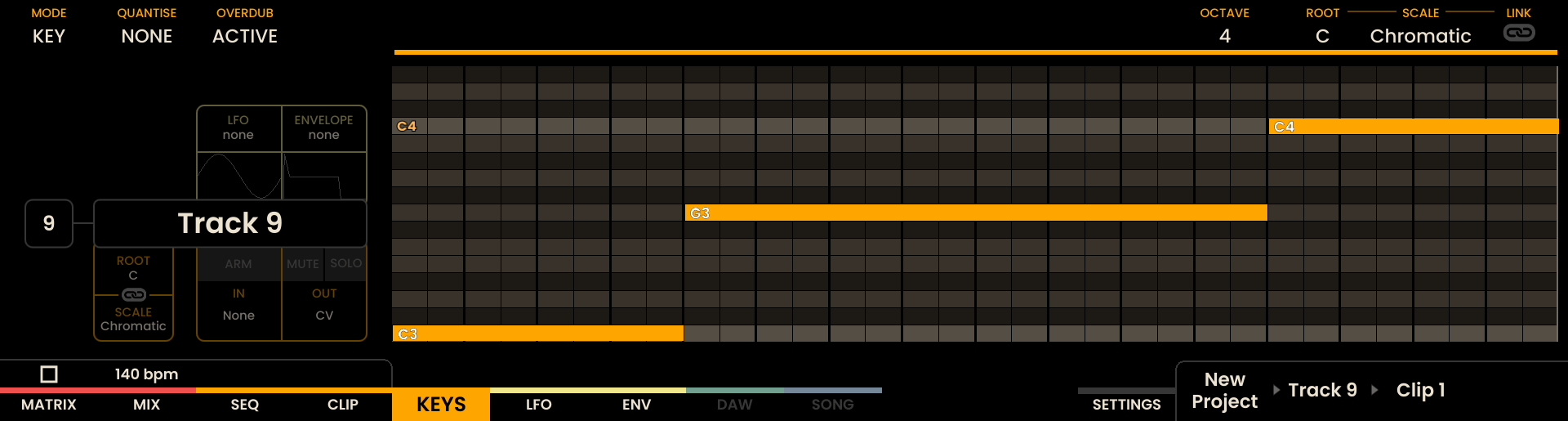
Interface Overview
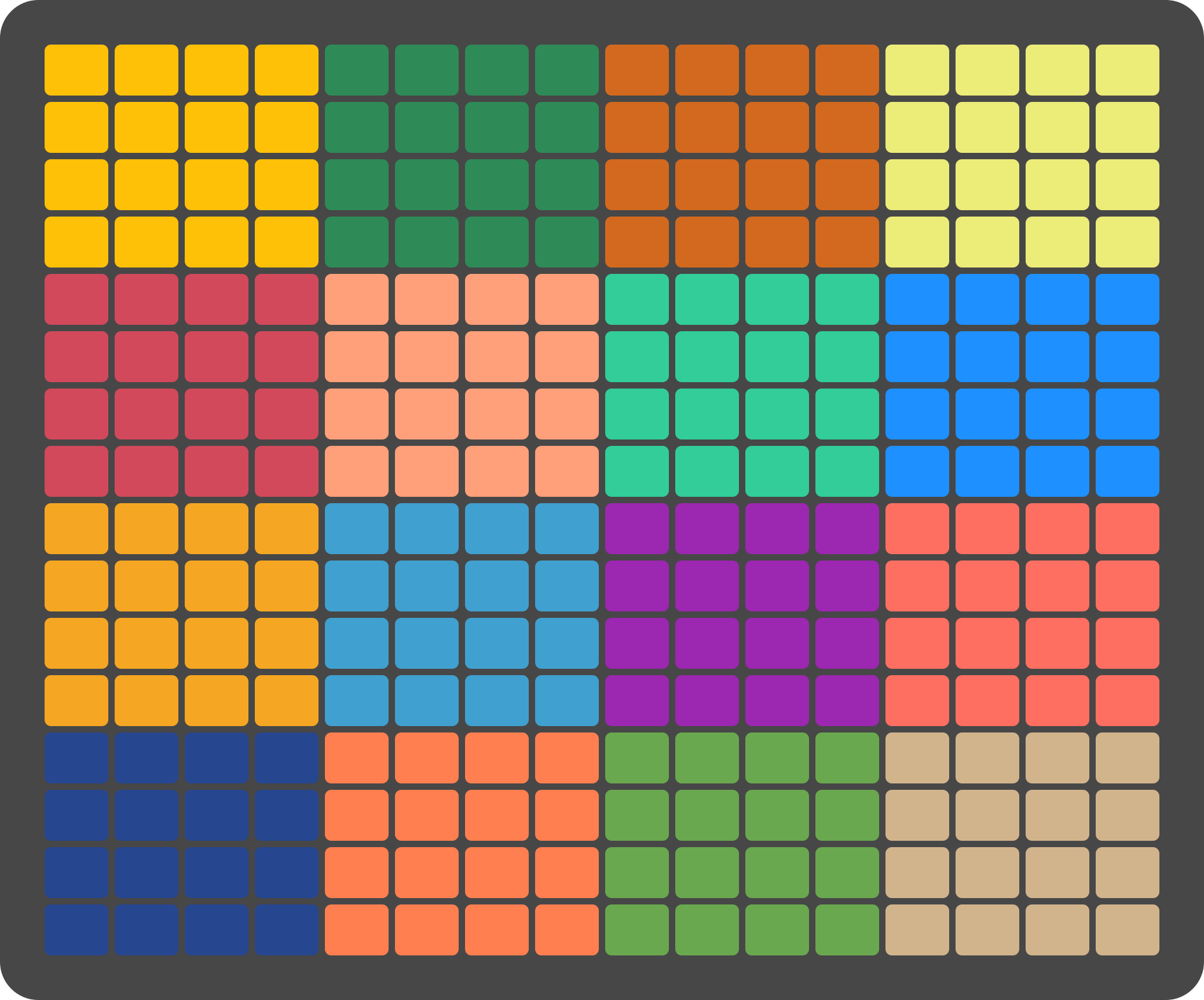
The Keys Page displays a piano roll showing the current recording or any pre-existing notes. At the top of the display, an overview of the recording settings for each track is shown. As notes are being recorded they will appear on the piano roll in real-time.
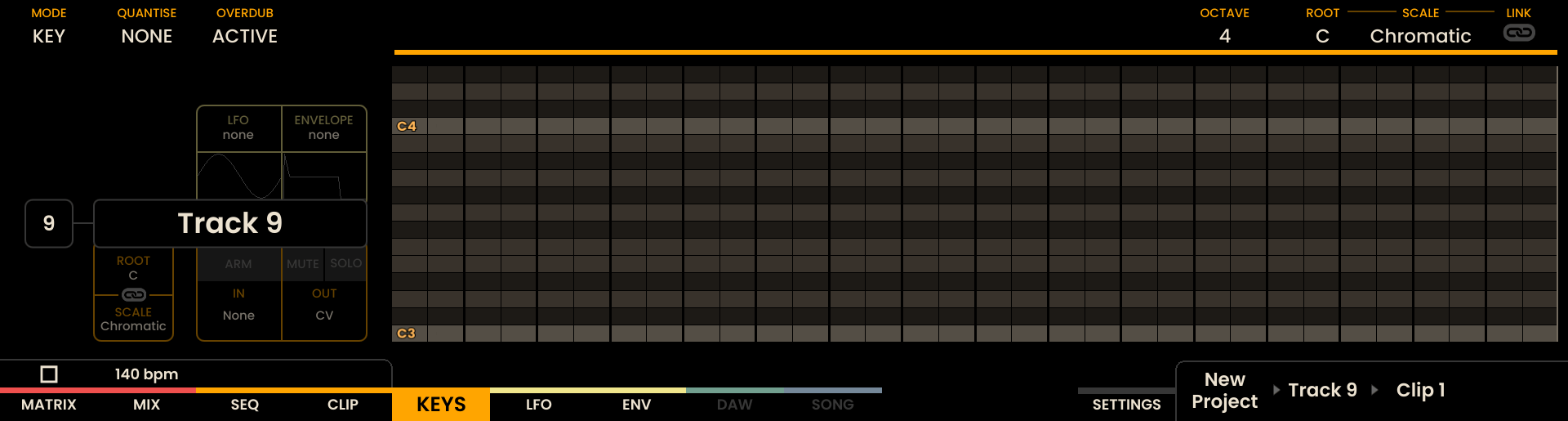
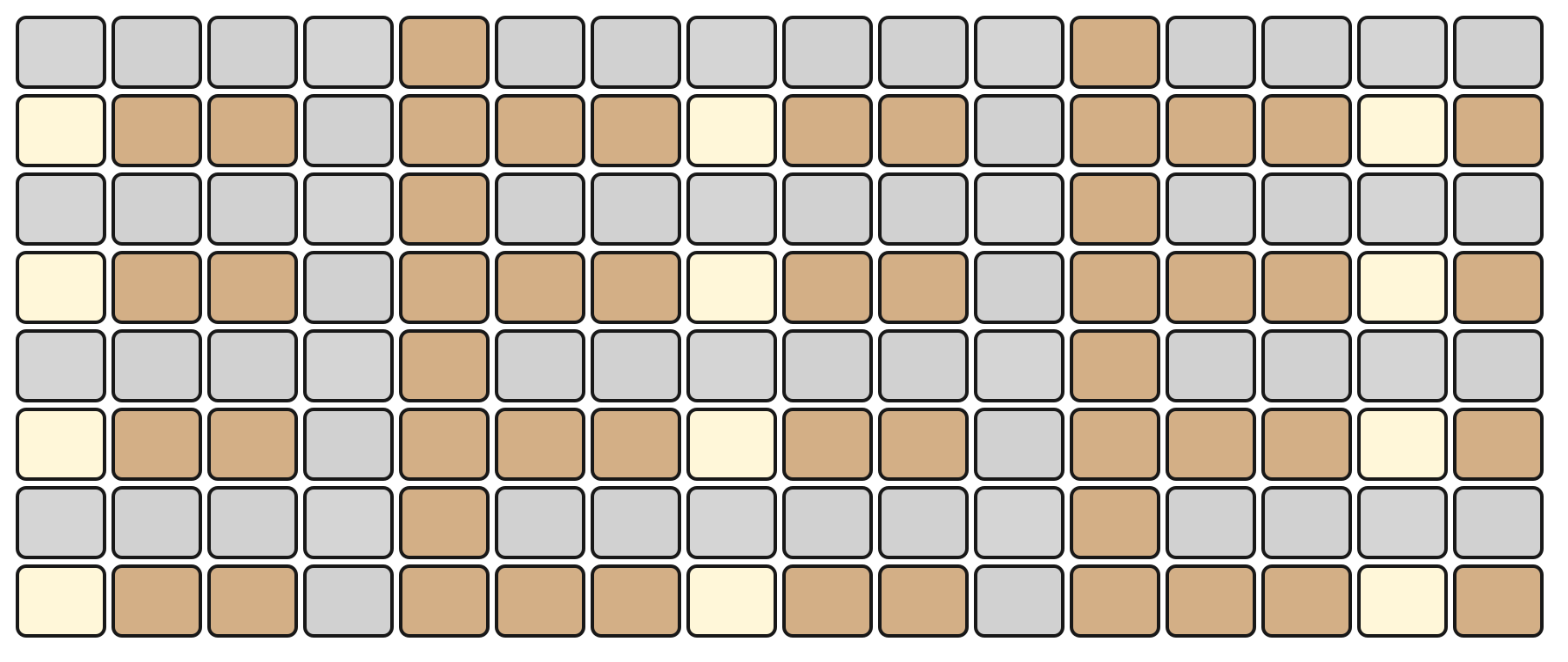
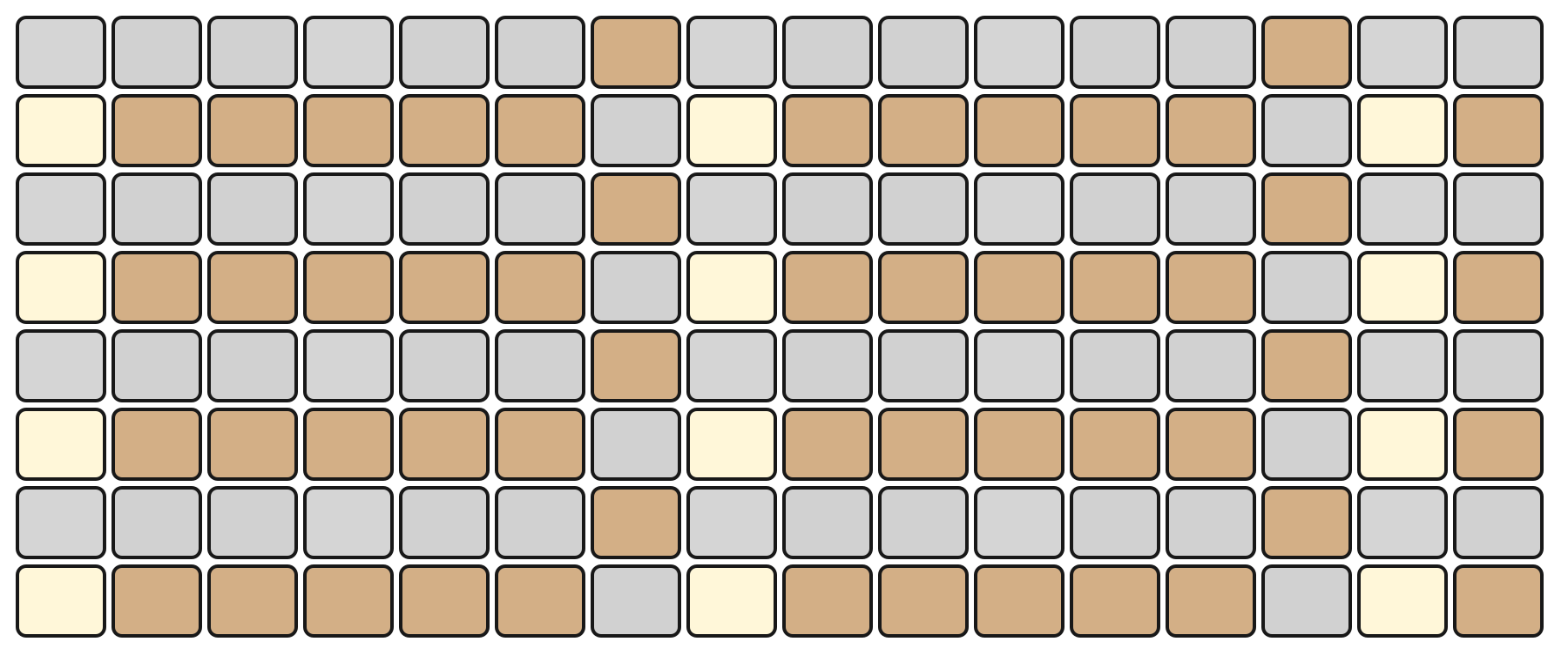
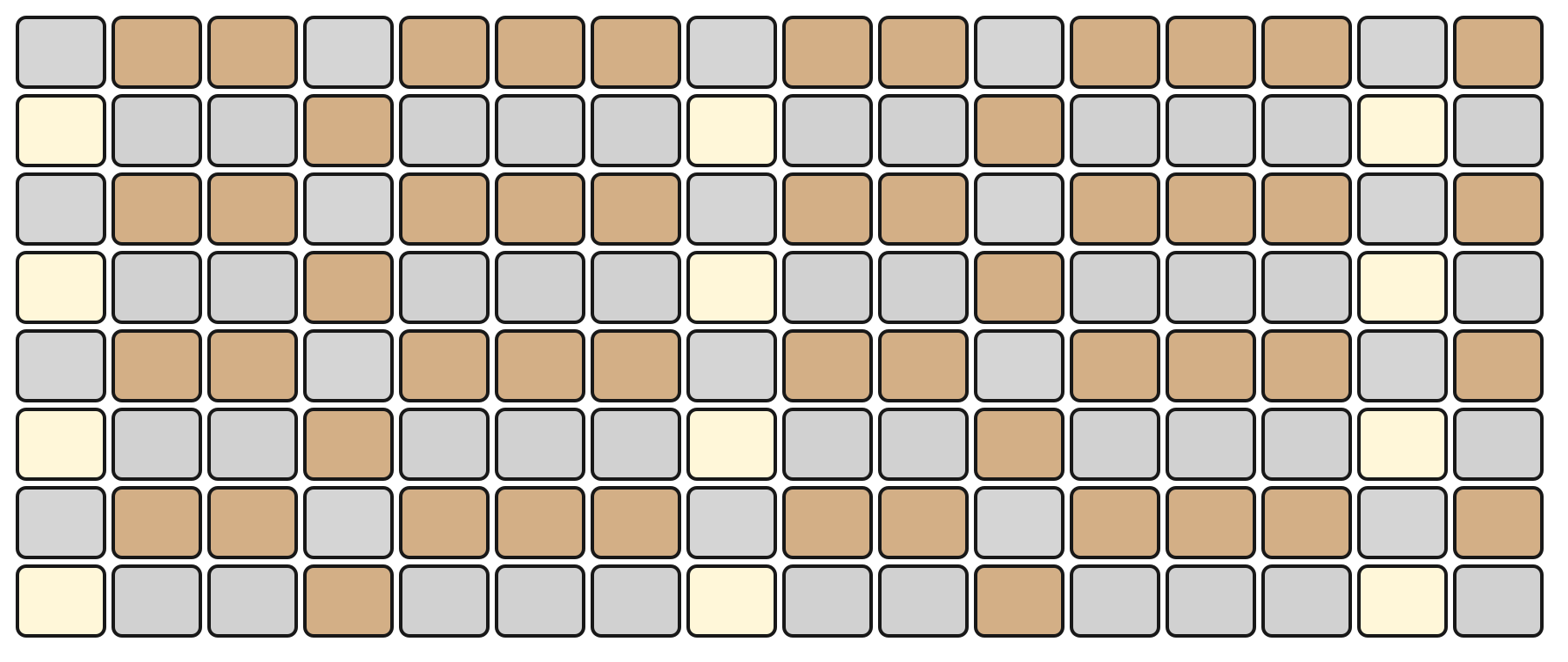
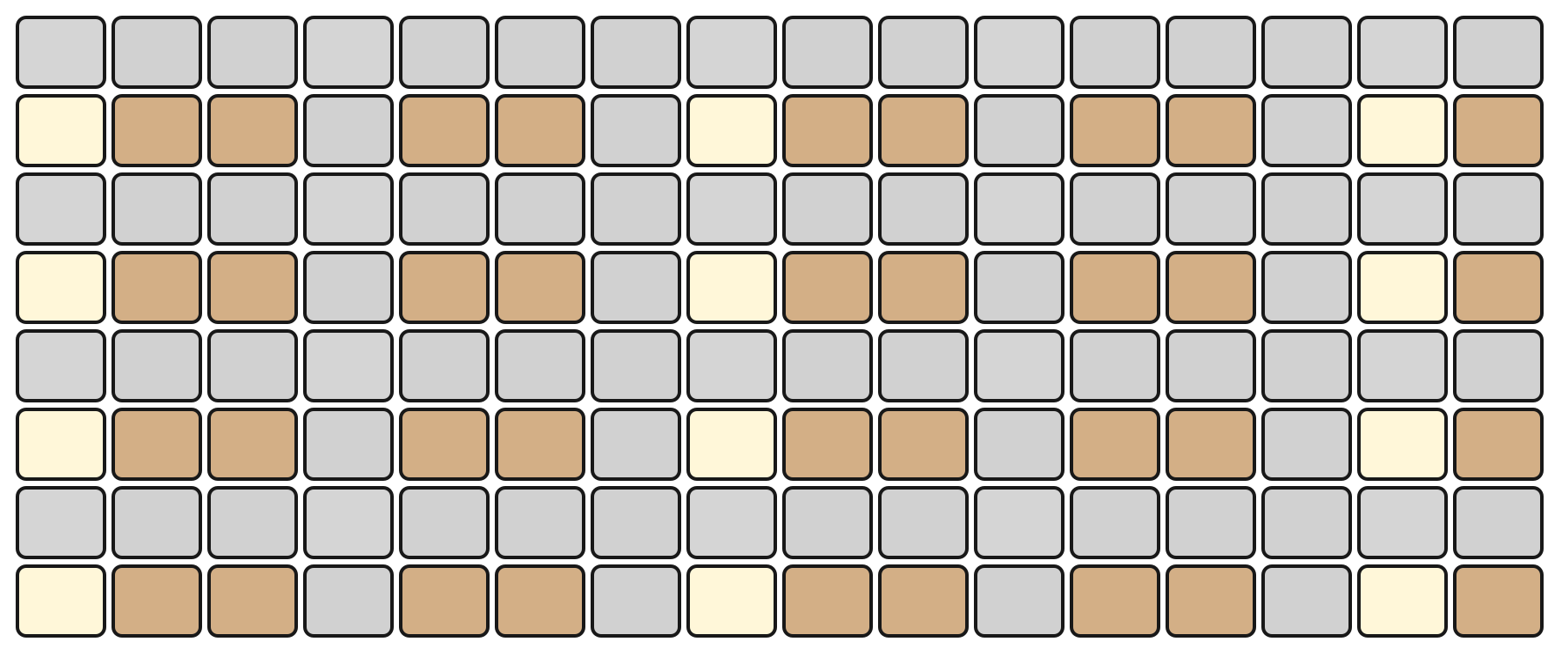
The Grid Pads are divided vertically into two sections:
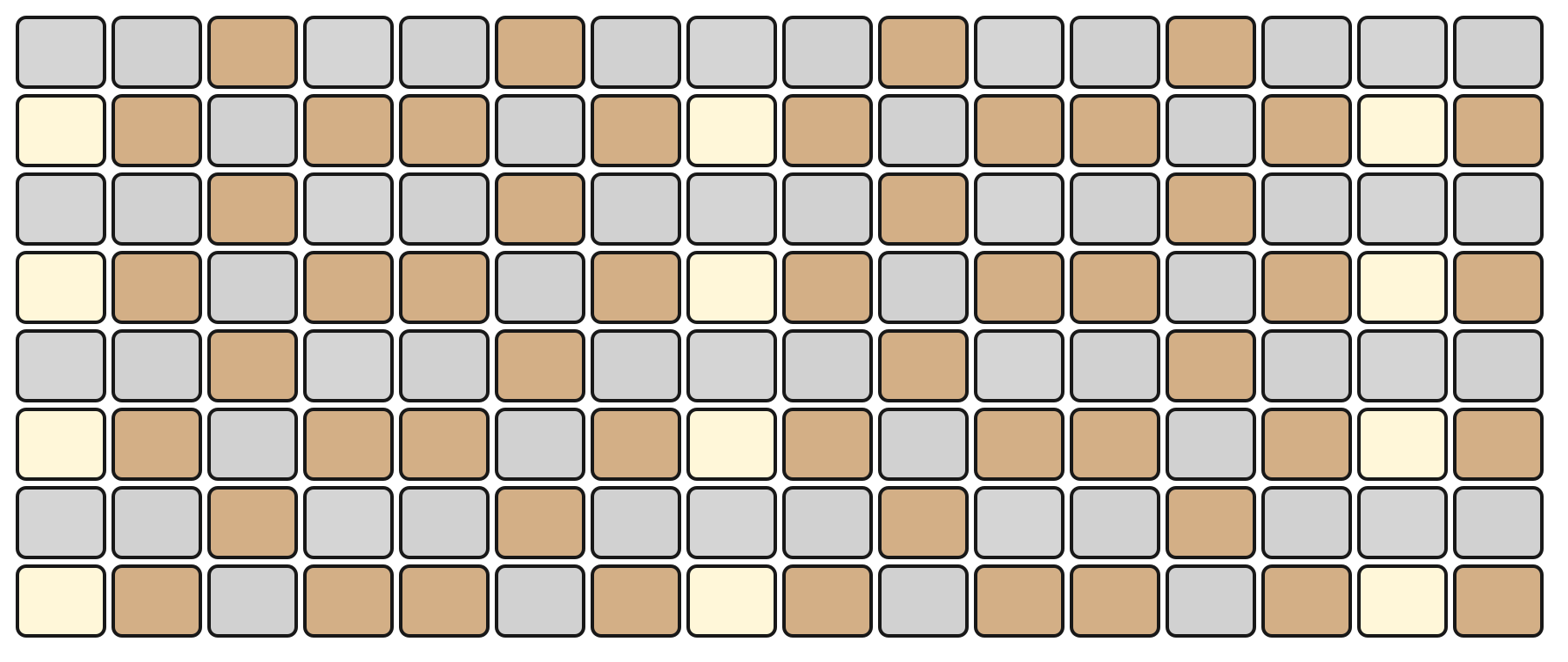
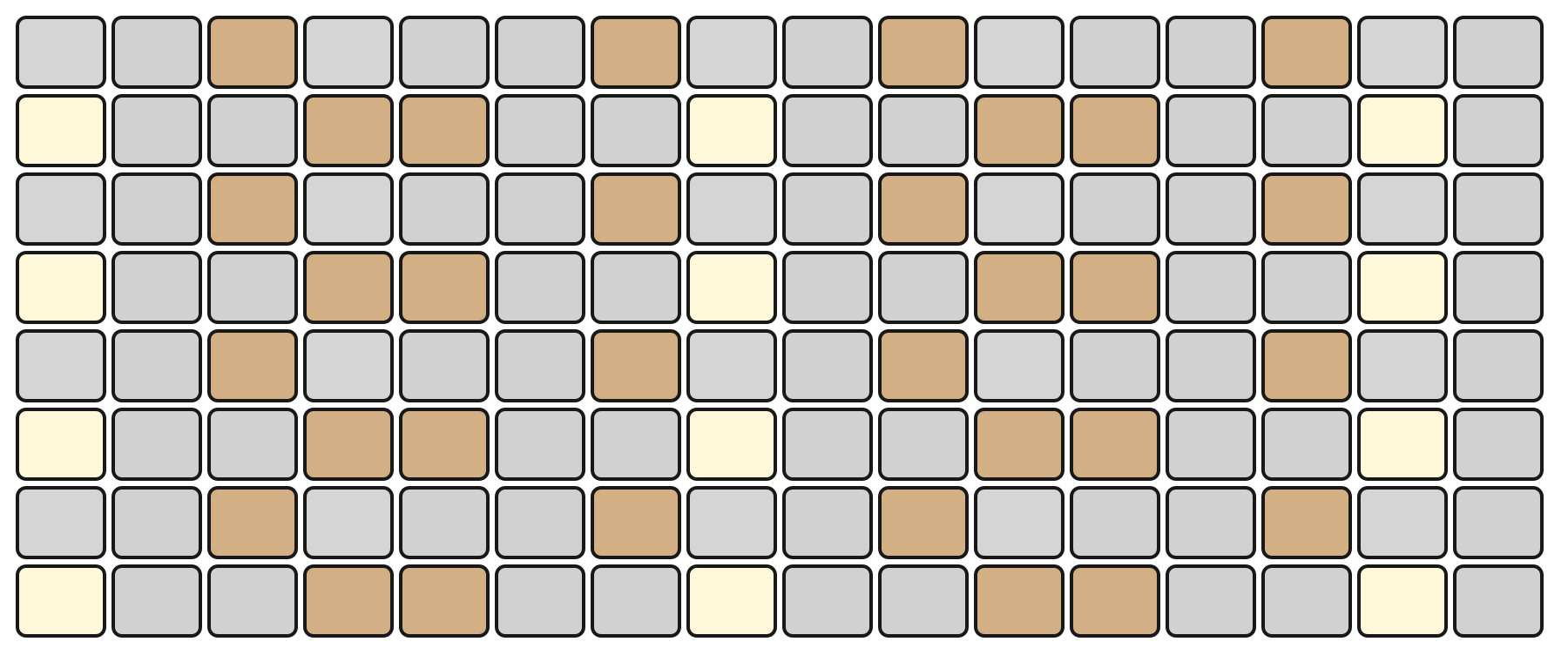
The top section represents notes by pitch, with the layout determined by the selected mode.
The bottom section represents velocity/modulation, mapped linearly from 0 to 127. Notes and velocity pads can be pressed simultaneously, enabling dynamic expression.
The root note of each octave is illuminated in white, while notes within the selected scale are shown in orange. Notes outside the scale are shown in grey.
For example, in KEY Mode, the top section represents the notes in a chromatic layout, while the bottom section represents the current velocity.
Track selection is achieved by pressing the Track Buttons on the left side of the Grid Pads . The selected track button will light up, and track information will appear on the display.
Recording Settings
By default, recordings are made at a resolution of 768 PPQN (pulses per quarter note). If the PPQN output setting is modified in the Settings Page, the recording resolution adjusts accordingly. These settings are displayed at the top of the screen and affect both Keys Page inputs and external device inputs (e.g., MIDI, USB).
Overdub
When OVERDUB is enabled, new notes are recorded on top of the existing notes in the track. If OVERDUB is disabled, the existing notes are replaced by the newly recorded ones. OVERDUB can be toggled by rotating the encoder above the OVERDUB label on the display.
Quantization
Quantization can be adjusted by rotating the encoder above the QUANTIZE label on the display .
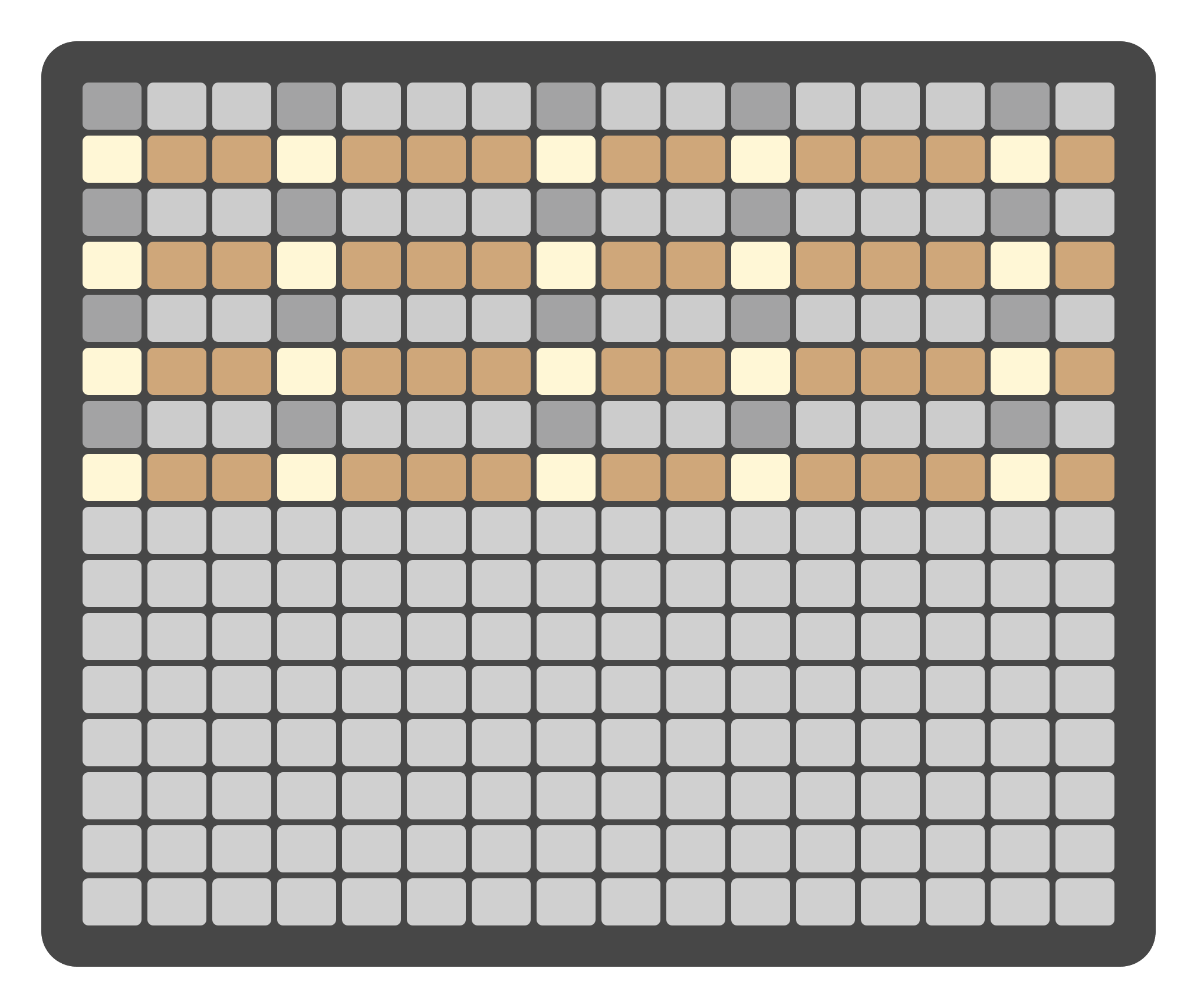
Quantization operates in a non-destructive manner and uses two parameters:
Quantization: Defines the rhythmic target value (e.g., 1/4, 1/8, 1/16).
Strength: Defines how strongly notes are pulled toward the selected rhythmic grid (0–100%).
At 100% Strength, notes are fully aligned to the selected quantization value. Lower Strength values partially move notes toward the grid while preserving aspects of the original timing.
Quantization settings can be applied during recording or adjusted after recording without permanently altering the original note positions.
Each Clip stores its own Quantization and Strength values. This allows different clips and tracks to use independent quantization behavior within the same project.
Quantization |
|---|
1/32 |
1/16 |
1/8 |
1/4 |
Keys Page Modes
Several modes are available on the Keys Page, each providing different layout options for note input.
KEY Mode
In KEY Mode, the top section of the Grid Pads simulates the layout of a traditional music keyboard with a chromatic arrangement. The bottom section represents the velocity of the current note, with values ranging from 0 to 127.

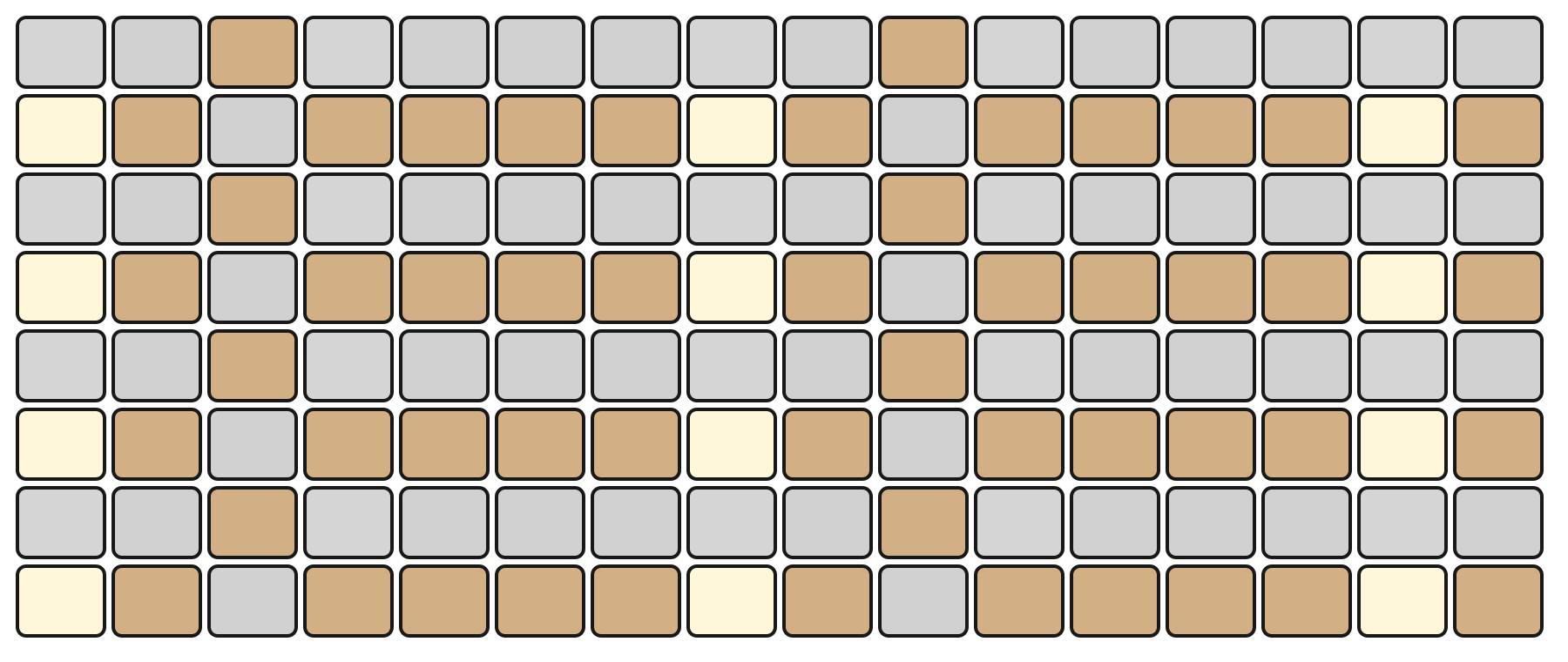
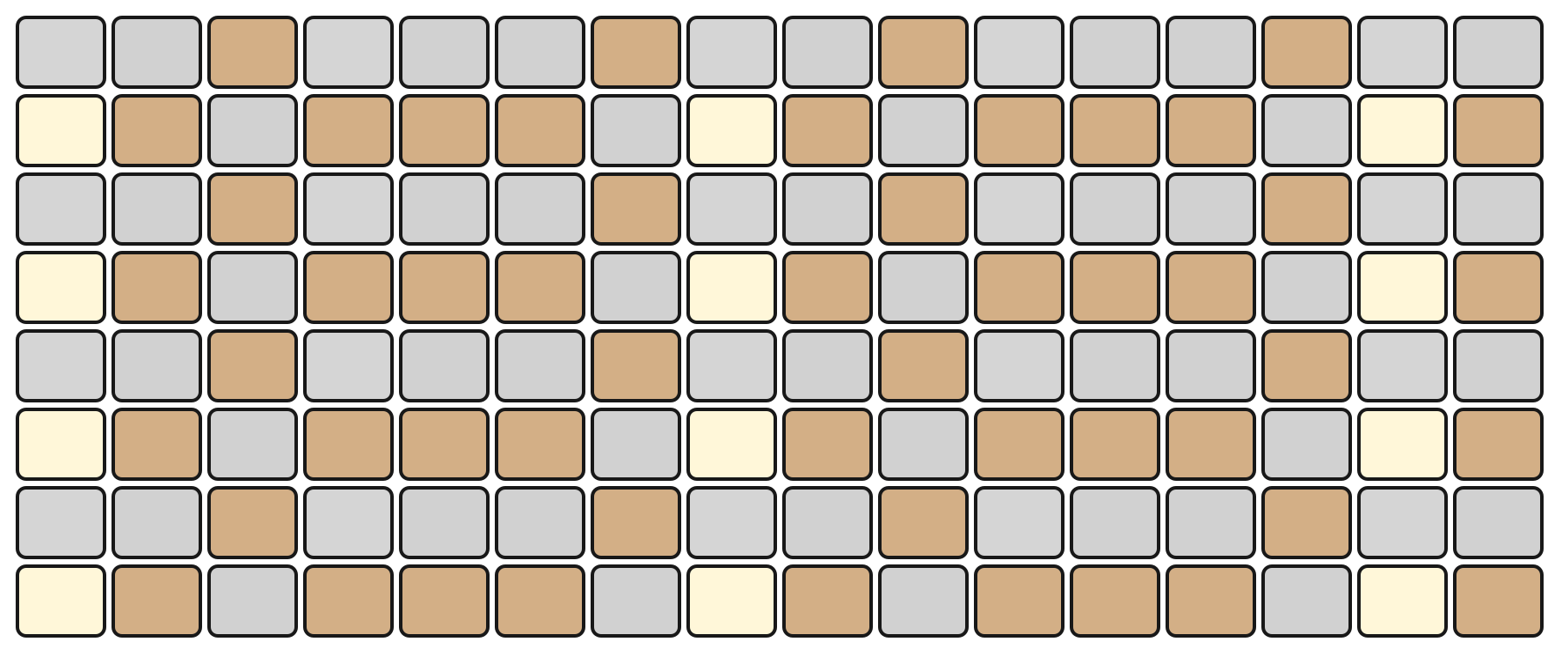
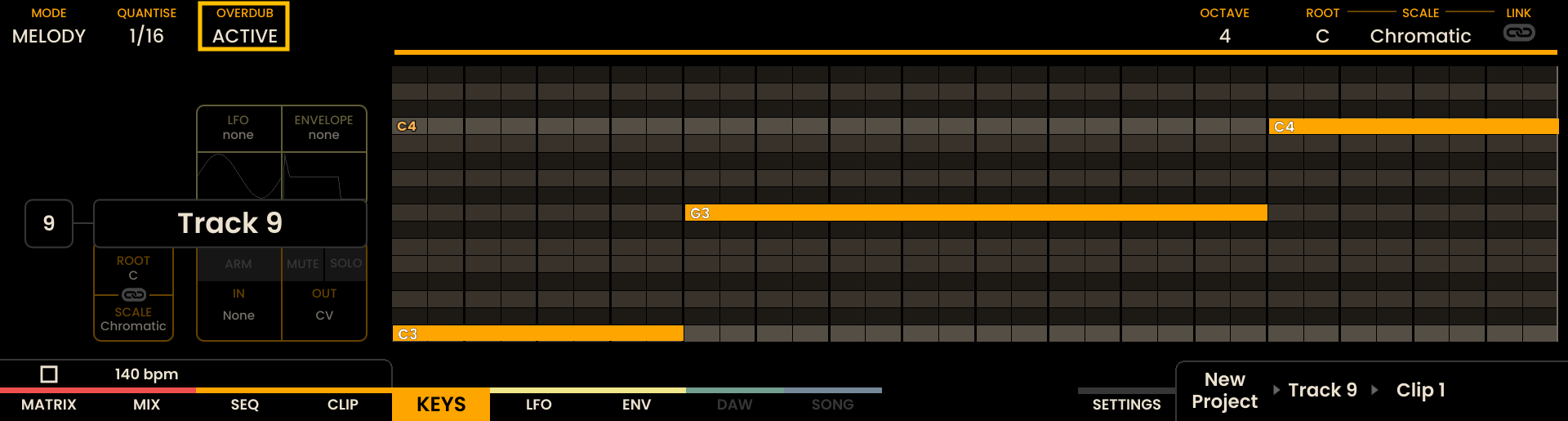
MELODY Mode
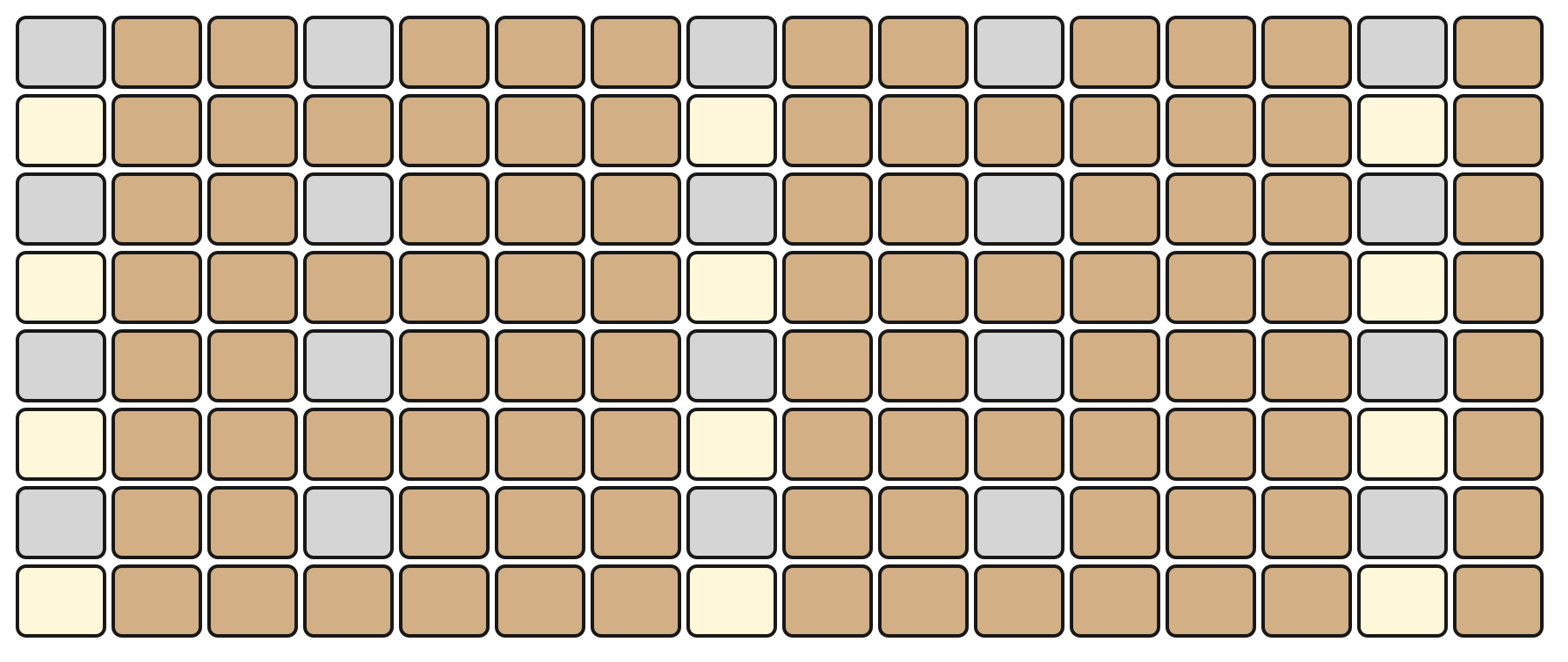
In MELODY Mode, the top section of the Grid Pads is arranged in an isomorphic layout. This layout maintains consistent interval patterns across different keys and octaves.
The bottom section represents velocity, with the same resolution as KEY Mode.
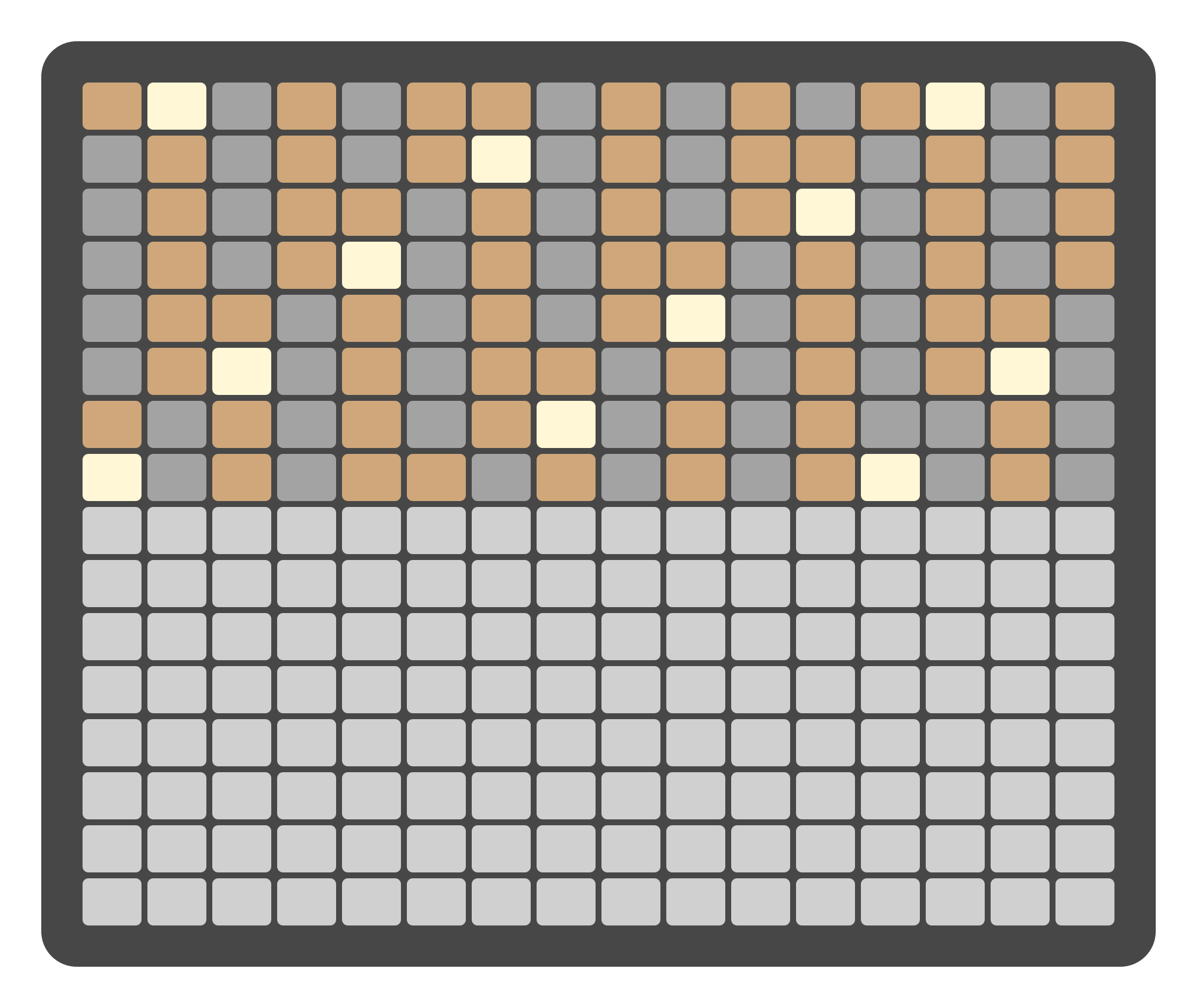
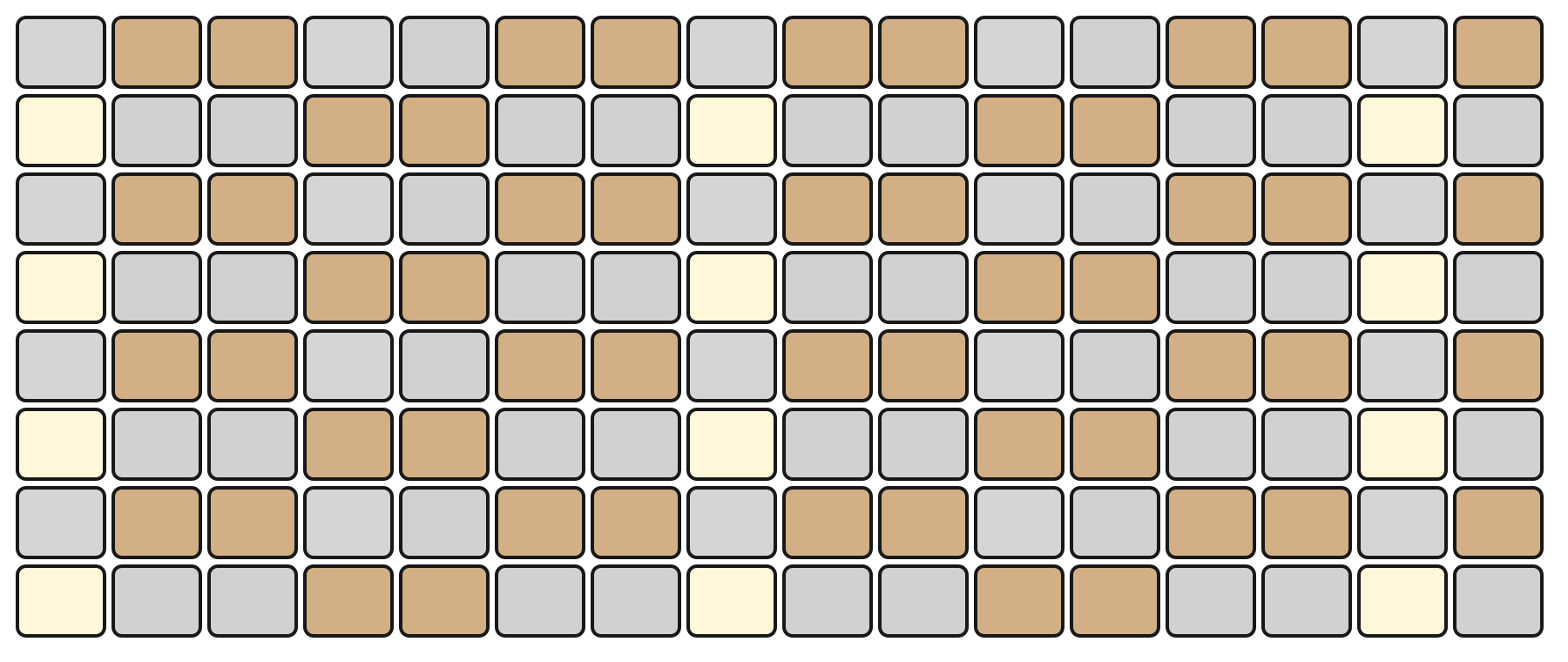
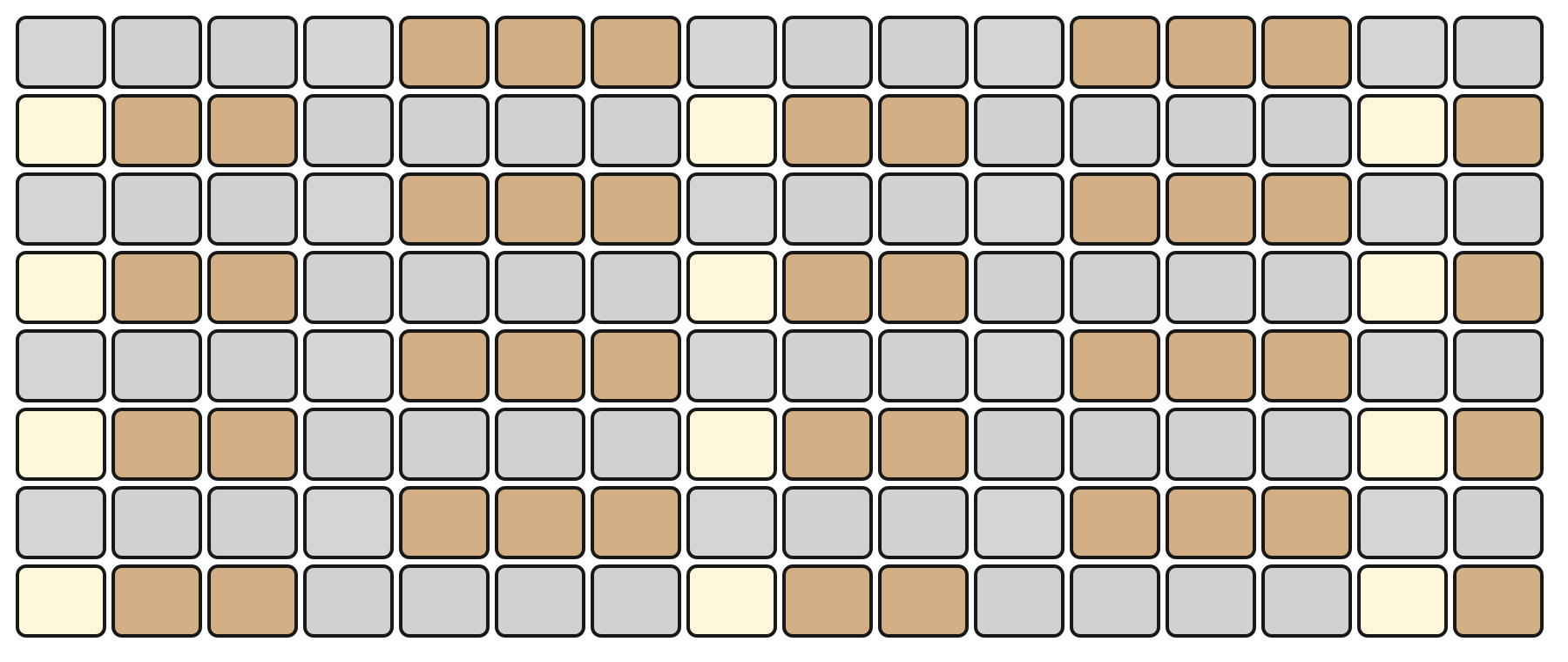
CHORD Mode
In CHORD Mode, the top section of the Grid Pads follows the Chord Picker layout. Each pad corresponds to a chord derived from the currently selected key and scale on the Keys page, allowing you to perform different harmonies directly from the grid.
The bottom section represents velocity, with the same resolution as in KEY and MELODY Modes. Velocity affects the overall loudness of the triggered chord.
Interaction in CHORD Mode mirrors the behavior of the Chord Piano Roll, with one key difference: chords triggered from this layout are played only and are not inserted into the Piano Roll. This makes CHORD Mode ideal for live performance and harmonic exploration without modifying the underlying sequence.
Chord Picker Views
Depending on the selected scale and track configuration, the Chord Picker can operate in two main views:
Chromatic Mode
In-scale Mode
These two views determine how chord roots are selected—either from the full chromatic set of notes, or from the degrees of the currently active musical scale.
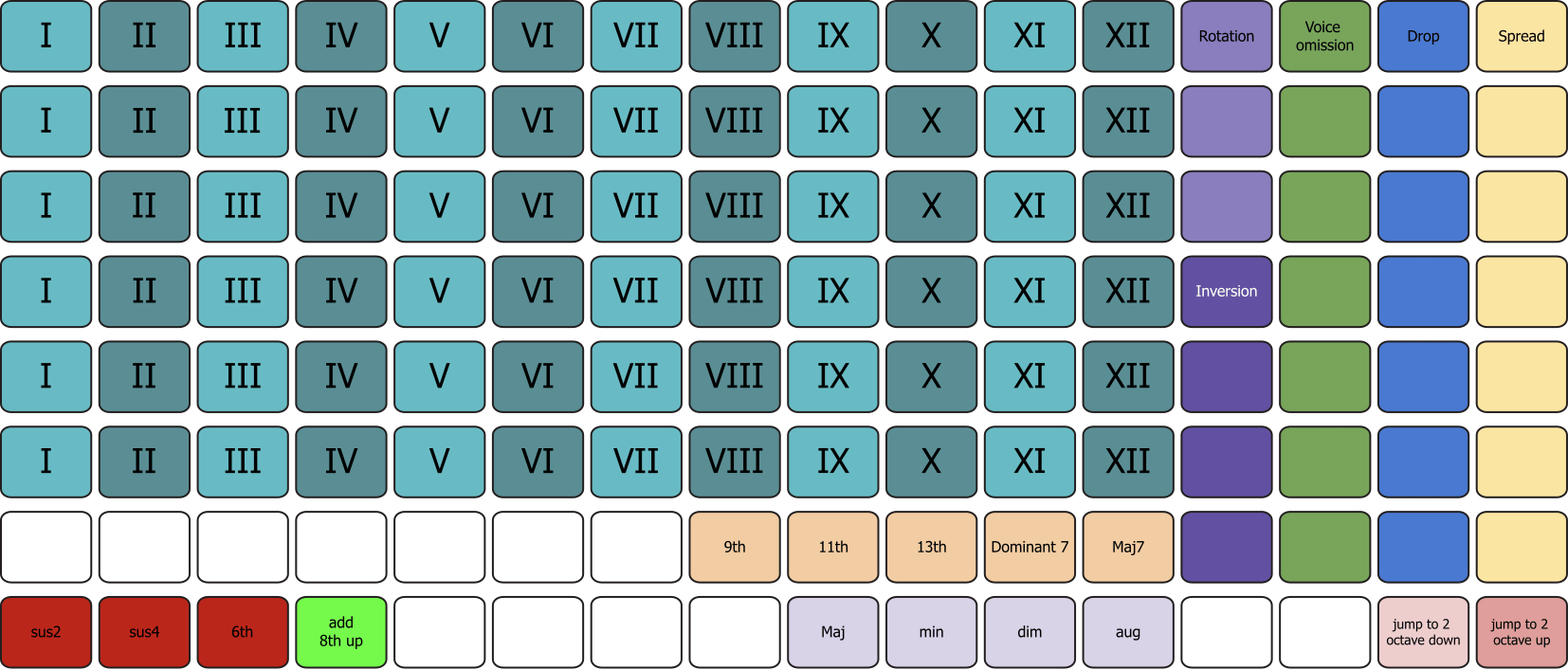
Chromatic Mode
In Chromatic Mode, chords are built freely from any of the twelve chromatic notes.
Before generating a chord, you first define its quality, alterations, and voicing parameters (inversions, spreads, drops, omissions) using the control columns on the right side of the picker.
To generate the chord:
Select the root note from the blue and light‑blue grid area at the top-left of the picker.
Each row represents an octave.
Each column represents a chromatic pitch from C up to B.
This layout lets you build any chord quality on any chromatic root, independently of the currently active track scale.
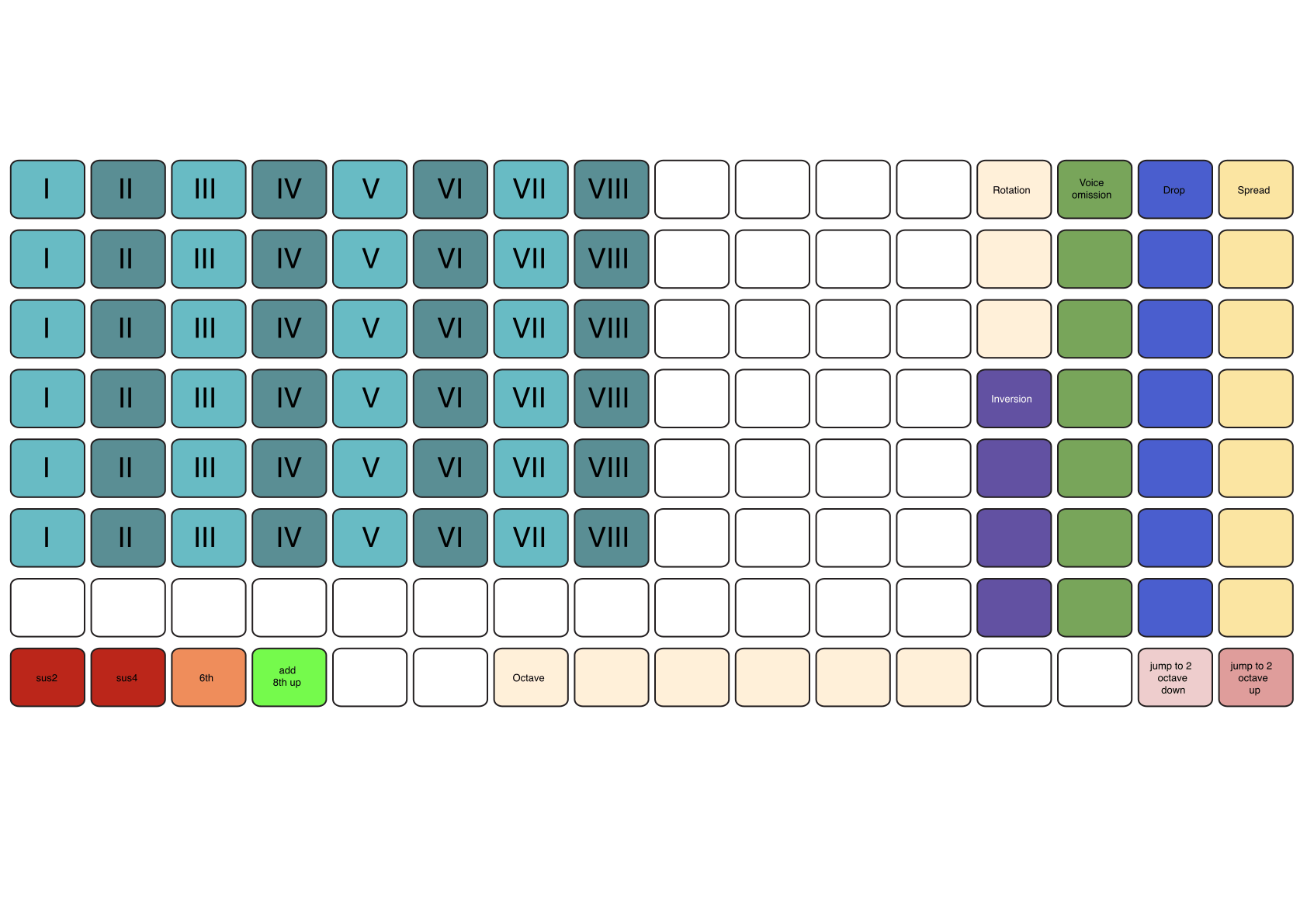
In-scale Mode
In In-scale Mode, chords are generated directly from the degrees of the selected scale, rather than from absolute chromatic notes.
In this view:
The blue/light‑blue pads represent scale degrees (I, II, III, …) that form the basis of the chord.
The number of available degrees depends on the currently selected scale.
Each row represents chord complexity, increasing from bottom to top:
Power chord (1 + 5)
Triad
7th
9th
11th
13th
This view is ideal for fast, harmonically consistent composition within a scale (e.g., I–IV–V or ii–V–I progressions).
Note
In both modes, a chord is generated only after its quality, extensions, and voicing options have been defined. Once these parameters are set, choosing a root note (Chromatic Mode) or scale degree (In-scale Mode) creates the chord for the selected step.
Common Chord Parameters
Both Chord Picker modes share a consistent set of voicing and shaping controls located in the right-most columns of the grid. These include:
Inversion
Rotation
Voice Omission
Spread
Drop
Alterations
Inversion and Rotation
Inversion and rotation controls are found in the pink/white column to the right of the picker.
From bottom to top:
The first pad = root position
The second pad = 1st inversion
The third pad = 2nd inversion
And so on…
Inversions never move extensions above the 7th (9, 11, 13). Selecting an inversion that exceeds the number of active chord voices simply has no effect.
The top three pads in this column apply rotations, which reorganize the chord by placing higher extensions (9th, 11th, 13th) at the bottom of the voicing. For example, rotating a Cmaj9 chord may move the 9th to the bass position and shift the rest upward.
Voice Omission
In the green column, each pad removes a specific chord tone:
Bottom pad = omit root
Next = omit 3rd
Next = omit 5th, etc.
This is useful for simplifying chords, creating open voicings, or thinning harmonic density.
Spread and Drop
The yellow column applies Spread: each pad raises the selected voice by one octave. The white column applies Drop: each pad lowers the selected voice by one octave.
Both columns include additional pads at the bottom for two-octave spreads/drops.
Alterations
The bottom-left of the picker provides four alteration options:
sus2
sus4
6th
Add octave of bass note
These allow flexible voicing and harmonic color adjustments for both diatonic and chromatic chords.
Scales
Scales can be adjusted by rotating the second encoder located above the SCALE label on the display. Reliq includes various scales, with detailed information available in the section at the end of this chapter.
Root Note
The Root Note can be changed by rotating the third encoder located above the ROOT label on the screen. This adjustment defines the base note of the selected scale.
Link
When LINK is enabled, the Root Note and Scale settings are inherited from the global one defined in the settings page. Disabling LINK allows for independent adjustment of the Root Note and Scale.

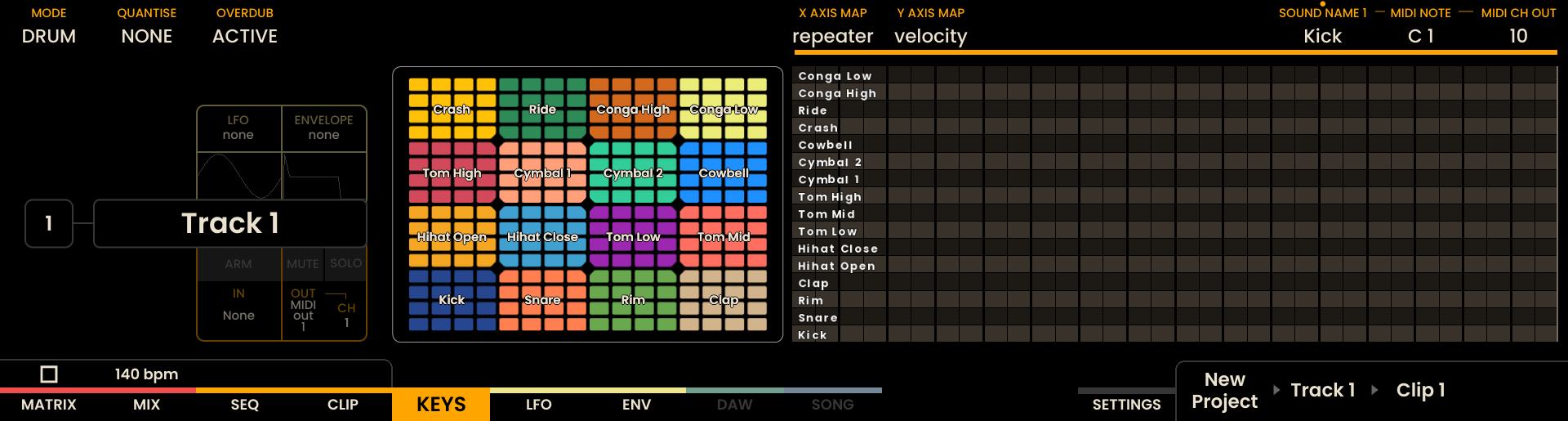
Sound Settings
The per-sound settings are available in the upper-right encoders on the KEYS page and mirror the controls in the Track Settings panel of the Sequencer Page. Use these encoders to edit:
SOUND NAME — select a kit sound and click the encoder to rename it.
MIDI NOTE — set the MIDI note number for the selected sound (note name/number shown).
MIDI CH OUT — select the MIDI channel (1–16) for that sound.

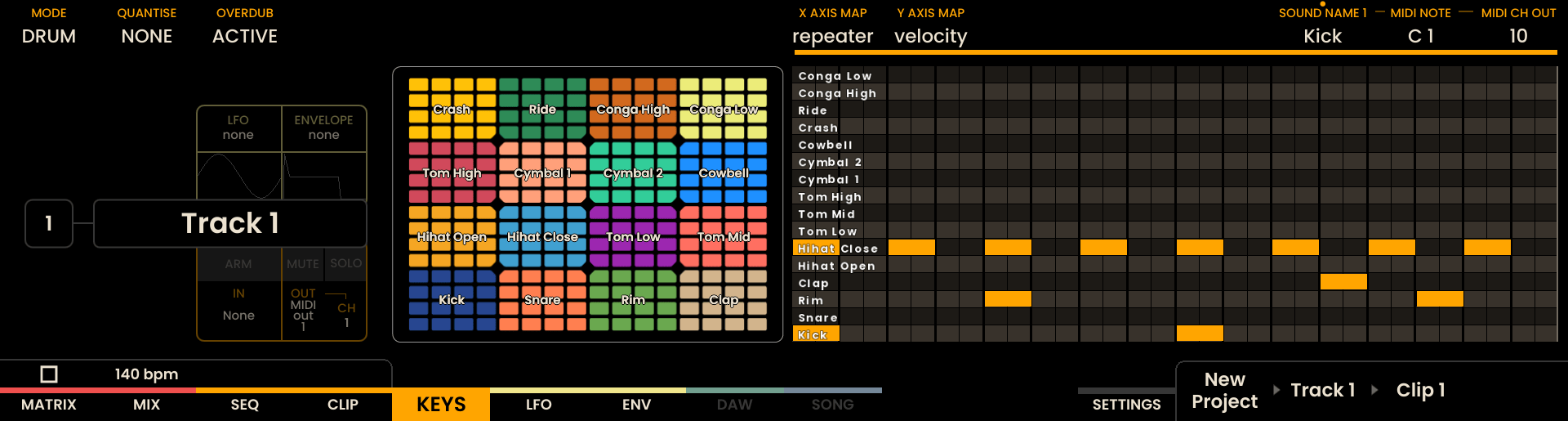
Pad Layout Controls
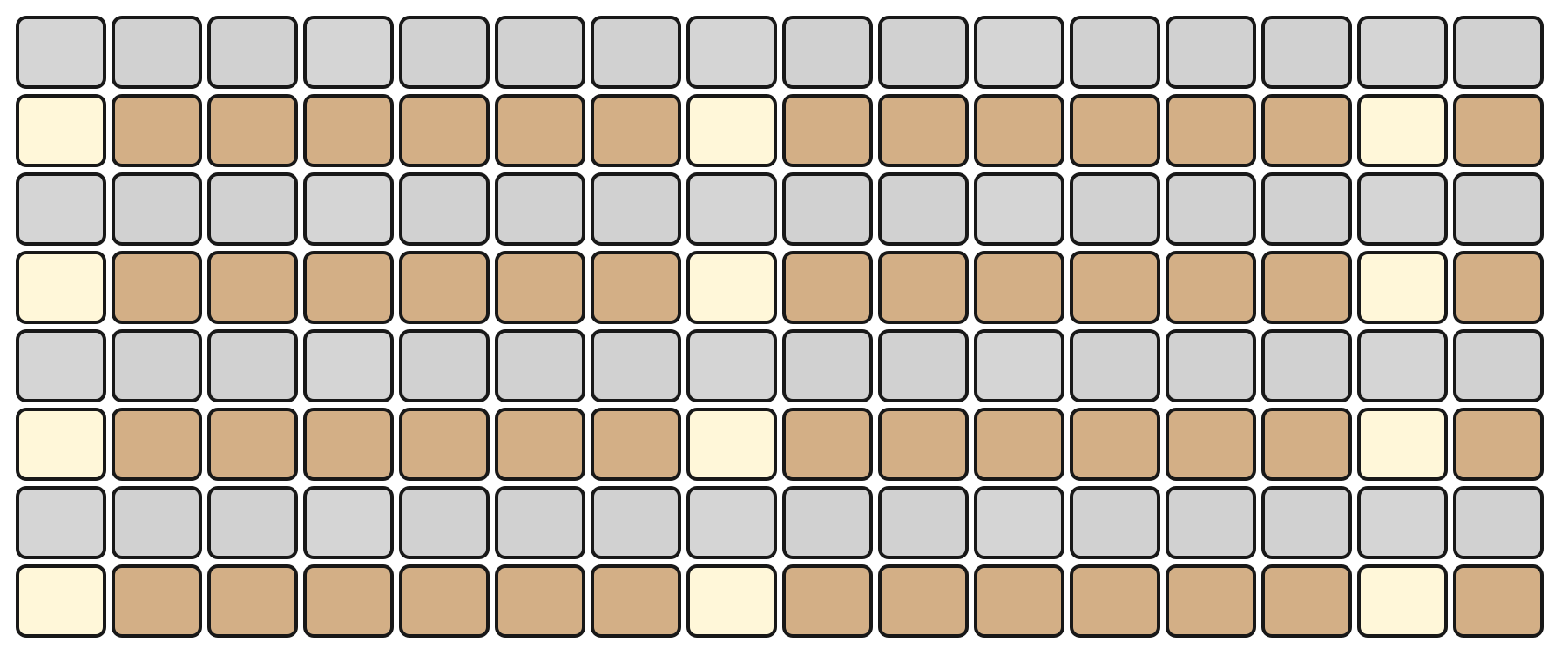
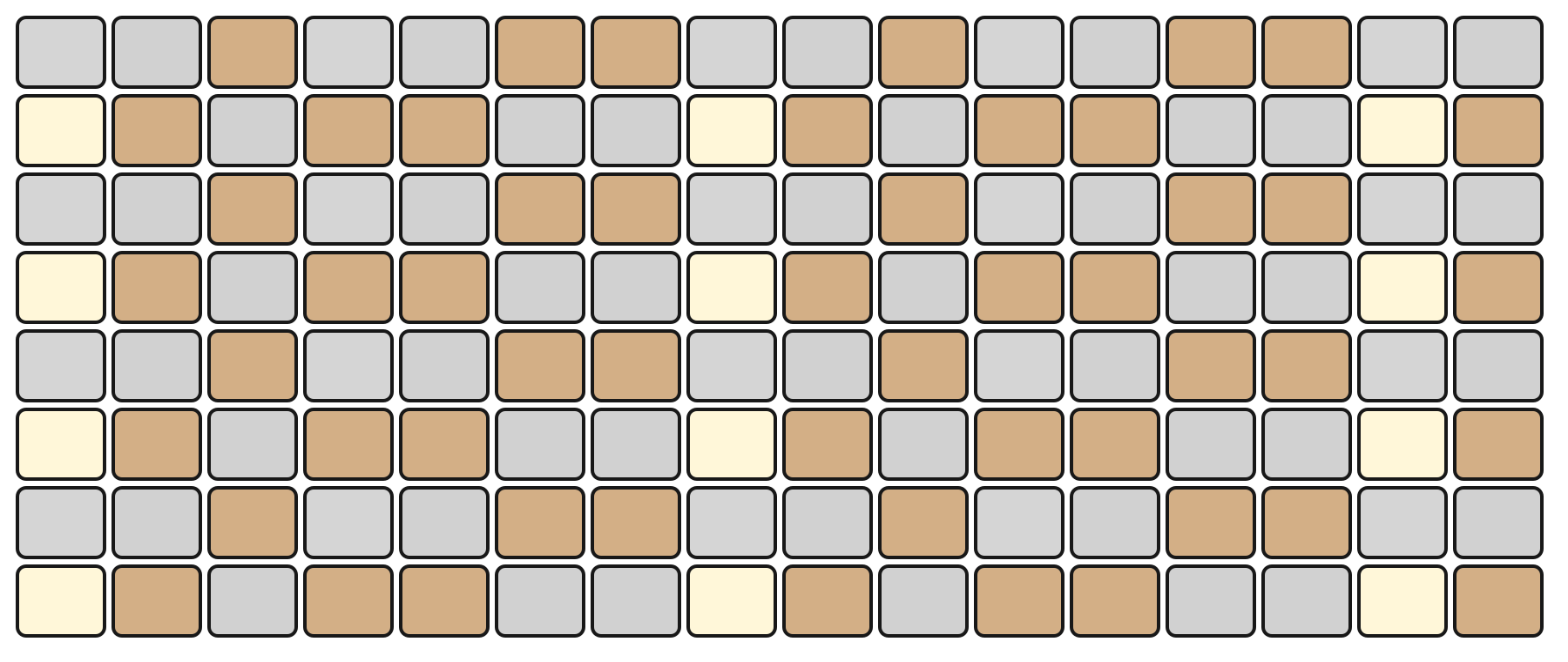
Two mapping options appear in the middle of the screen for the 4×4 pad block of each sound: X AXIS MAP and Y AXIS MAP. Each axis can be set to one of the following modes:
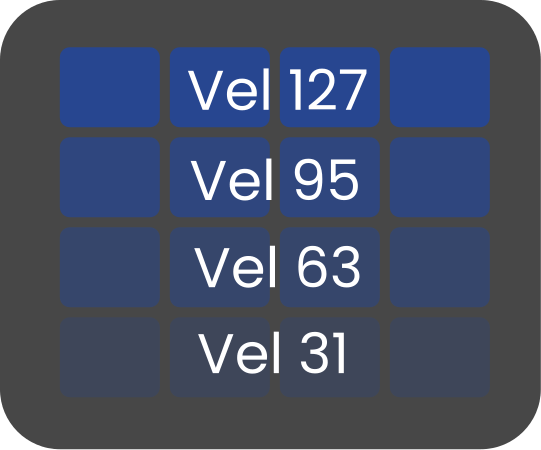
Velocity
Maps the axis to velocity values. For example, if Y AXIS MAP is set to Velocity the bottom row of the 4×4 block will send the minimum velocity and the top row the maximum velocity. The same applies to the X axis.
If both X and Y axes are set to Velocity the combined mapping provides finer velocity resolution (sixteen stepped levels across the pad block).
Velocity on Y Axis
Repeat
Maps the axis to note repeats at musical subdivisions. For example, with X AXIS MAP set to Repeat the leftmost column will play a single-shot hit, the next column will repeat the hit on 1/8 notes, the third on 1/16 notes, and the fourth on faster 1/32 repeats.
If both X and Y axes are set to Repeat the highest value is applied.
When using Repeat pads, the played repeat pattern is recorded as discrete events in the sequencer (each repeated hit is recorded as its own event).

Repeat on X Axis
Using these two axis maps you can create expressive pad performances that combine dynamic velocity control with rhythmic repeats directly from the Keys page.
Per-Sound Solo and Mute
Individual drum sounds can be muted or soloed directly from the KEYS page.
To mute or solo a sound:
Press and hold MUTE or SOLO.
While holding the button, press any pad belonging to the desired drum sound.
The mute or solo state applies to the entire sound, regardless of which pad in its 4×4 block is pressed.
Muting individual drum sounds is available only from the KEYS page.
Monitoring in Keys Mode
The KEYS page allows note input on the selected track, which can be changed using the track buttons . The KEYS page will play and output notes regardless of the track’s ARM state.
Recording in Keys Mode
To begin recording, ARM Reliq by pressing the Record Button. The button will illuminate red when recording is active.
Any ARMED tracks will record from their specified inputs. Only the selected track will record from the notes played on the KEYS page pads, regardless of the ARM state of the track.
Keys Functions Overview
Overdub: Overwrite or layer new notes onto existing ones.
Quantize: Adjust the precision of note timing.
KEY Mode: Chromatic note layout with velocity control.
MELODY Mode: Isomorphic layout for intuitive, scale-based input.
CHORD Mode: Play chords based on selected key and scale.
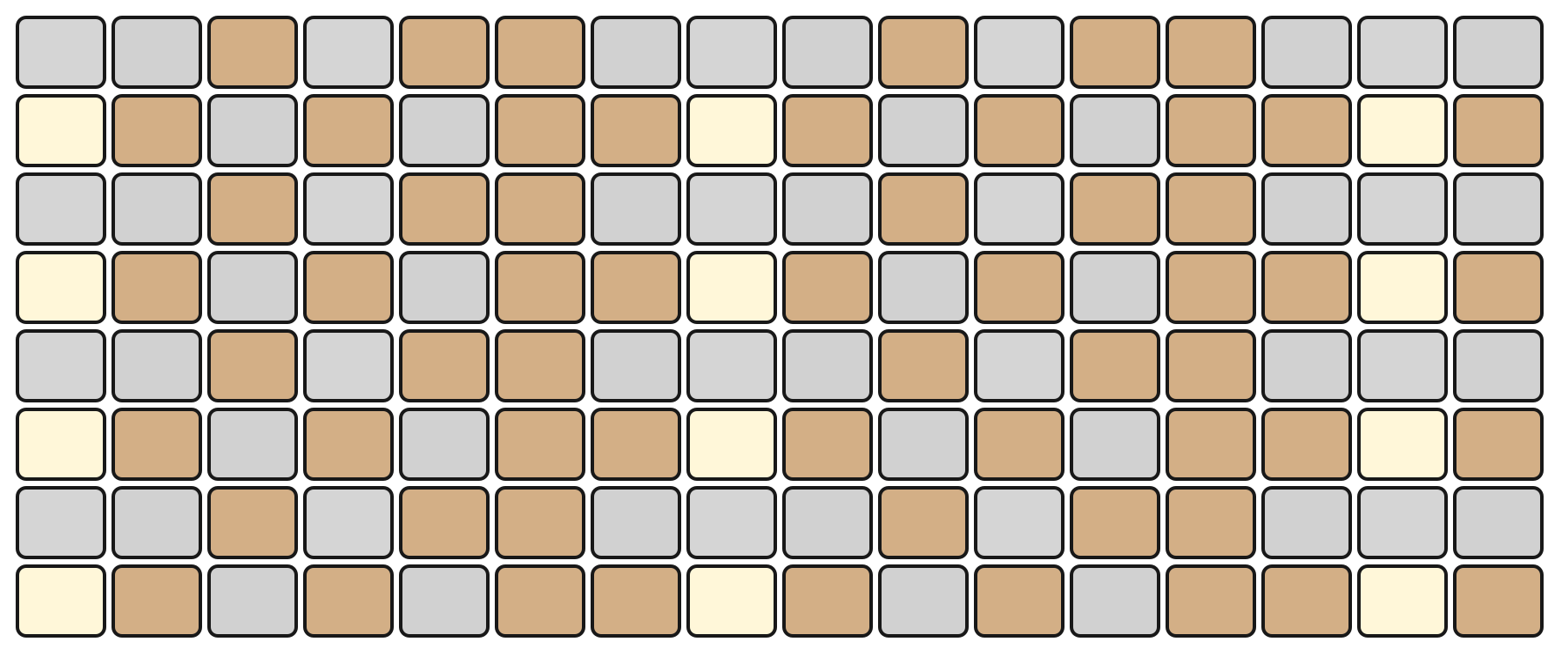
DRUM Mode: 16-pad drum kit layout with velocity and repeat mapping.
Scales: Adjust available musical scales.
Root Note: Define the base note of the selected scale.
Link: Enable or disable linking of Root Note and Scale settings to the global settings.
Octave Navigation: Shift octaves during performance.
Available Scales
All scales available in Reliq are listed below, a Root note of C is used as a reference for each scale.